The Menstruation Cycle is a natural monthly process in the female body, preparing for the possibility of pregnancy. It involves changes in hormones, the ovaries, and the uterus. Most girls have their first period around the age of 10 to 14, which is called menarche. The menstrual cycle continues until menopause, usually between 45 to 55 years of age. A typical cycle lasts 28 days, but anything between 21–35 days is considered normal, as every woman’s body is different.
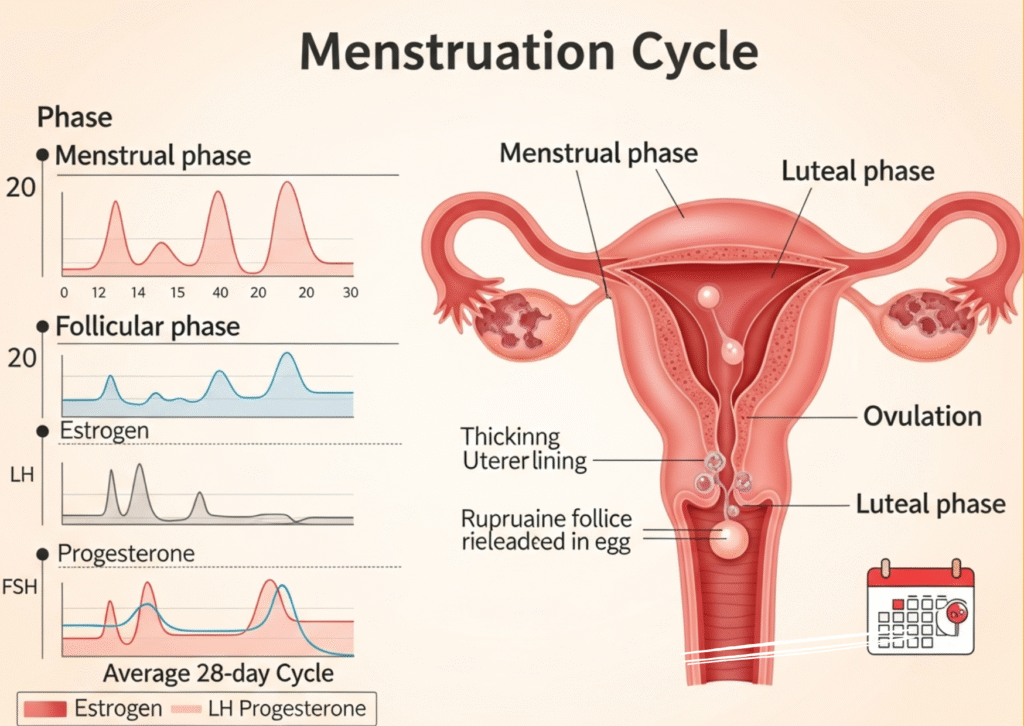
Four Main Phases of the Menstruation Cycle
Menstruation Phase
The menstruation phase begins when pregnancy does not occur, causing the uterus to shed its lining. This lining leaves the body as menstrual blood through the vagina. It usually lasts 3 to 7 days. Hormone levels of estrogen and progesterone are low, which can lead to cramps, lower back pain, mood changes, and tiredness. The purpose of this phase is to clear the old lining so the body can prepare for a new reproductive cycle. Good hygiene, rest, warm compresses, and hydration help manage discomfort during this time.
Follicular Phase
The follicular phase begins on the first day of menstruation and continues for about 13 to 14 days. During this phase, the pituitary gland releases FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone), which helps several follicles in the ovaries grow, but only one will usually mature into an egg. Meanwhile, estrogen levels rise, causing the uterine lining to rebuild and thicken in preparation for a possible pregnancy. This phase represents a period of renewed energy and emotional balance for many individuals as hormone levels gradually increase.
Ovulation Phase
Ovulation is the release of the mature egg from the ovary, usually around day 14 of a 28-day cycle. A sudden spike in LH (Luteinizing Hormone) triggers the egg to be released into the fallopian tube, where it may meet sperm for fertilization. This is the most fertile phase, meaning it is the time when pregnancy is most likely to occur if intercourse happens. Some people may notice signs like a slight rise in body temperature, clearer slippery cervical mucus, or mild cramps on one side of the lower abdomen. Ovulation lasts for a short period about 24 hours.
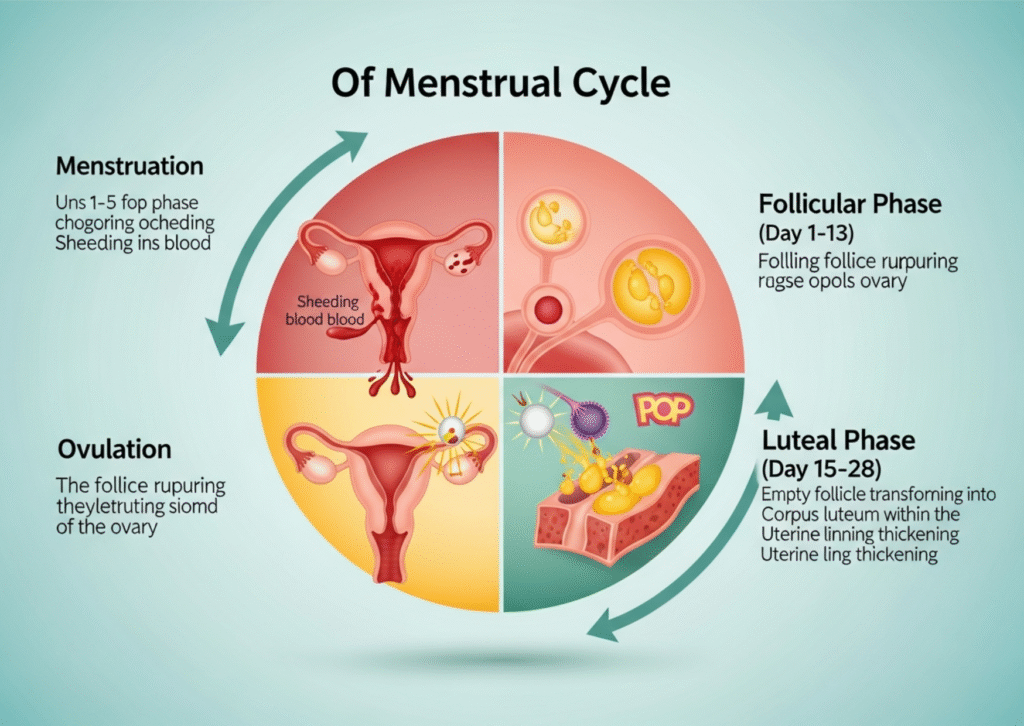
Luteal Phase
After ovulation, the empty follicle transforms into a structure called the corpus luteum, which releases progesterone. This hormone thickens and stabilizes the uterine lining, making it ready to support a fertilized egg. The luteal phase lasts about 12 to 14 days. If fertilization does not occur, the corpus luteum breaks down, causing progesterone levels to drop. This hormonal change triggers symptoms like bloating, mood swings, cravings, breast tenderness, or headaches, commonly known as PMS (Premenstrual Syndrome). The drop in hormones signals the uterus to shed its lining again, returning to the menstruation phase, and the cycle repeats.
Also read about this: Menstruation Cycle
Remember: https://healthytipspro.com/mental-disorder-illness/
Important Hormones and Their Roles
| Hormone | Role in the Cycle | |||||
| Estrogen | Builds the lining of the uterus and supports egg growth. | |||||
| Progesterone | Maintains the uterus lining after ovulation. | |||||
| FSH | Stimulates follicles (eggs) to develop in the ovaries. | |||||
| LH | Triggers the release of the egg during ovulation. | |||||
Simple Memory Trick:
| Phase | Key Hormone | Simple Explanation |
| Early Cycle | FSH | Prepares the egg |
| Before Ovulation | Estrogen | Prepares the uterus |
| Ovulation | LH | Releases the egg |
| After Ovulation | Progesterone | Protects the uterus lining |
Common Symptoms During Menstruation Cycle
- Cramps and lower abdominal pain
- Mood swings or irritability
- Fatigue and tiredness
- Headaches
- Breast tenderness
- Bloating
- Emotional sensitivity
These symptoms are usually normal. However, it is important to pay attention when symptoms become severe.
Normal vs. Abnormal Signs During the Menstruation Cycle
Understanding what is normal and what is not can help identify menstrual health problems early. Every girl or woman’s cycle may vary slightly, but certain patterns are considered healthy.
Normal Signs
These symptoms are common and usually not a cause for concern, as they occur due to natural hormonal changes:
| Normal Sign | What It Means |
| Cycle length between 21–35 days | Natural variation in monthly cycle timing |
| Bleeding lasting 3–7 days | Normal duration of menstrual flow |
| Mild to moderate abdominal cramps | Uterus contracting to shed its lining |
| Light to moderate bleeding (changing 3–5 pads/day) | Normal flow quantity |
| Breast tenderness before periods | Due to rising progesterone levels |
| Mild mood changes / sensitivity | Normal emotional response to hormonal shifts |
| Small blood clots (size of rice or small grapes) | Normal part of blood shedding |
These symptoms usually improve with rest, hydration, warm compression, or pain relievers.
Abnormal Signs (Need Medical Attention)
These symptoms may indicate an underlying health issue and should not be ignored:
| Abnormal Sign | Possible Concern |
| Period missing for 3+ months (not pregnant) | Could indicate PCOS, hormonal imbalance, stress, thyroid issues |
| Very heavy bleeding (changing pad every 1–2 hours) | May indicate menorrhagia or fibroids |
| Severe cramps that interfere with daily activities | Suggests dysmenorrhea or endometriosis |
| Large blood clots (bigger than a coin) | Possible uterine lining abnormalities |
| Periods lasting more than 7 days | Could signal hormonal imbalance or infection |
| Extreme mood swings, depression, or rage before periods | May be PMDD (severe hormonal mood disorder) |
| Irregular cycles every month | May be PCOS, thyroid problems, or stress-related |
| Severe acne, sudden hair loss, or facial hair growth | Often linked to PCOS or hormonal imbalance |
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical help if you experience:
- Pain that makes you skip school or work
- Bleeding that soaks pads too quickly
- Periods that stop suddenly or become very irregular
- Severe mood disturbances, panic, or depression during cycle
These signs are not normal and require evaluation by a Gynecologist or Endocrinologist.
Common Menstruation Cycle Disorders
Dysmenorrhea (Painful Periods)
- Cause: Strong uterine contractions or hormonal imbalance.
- Symptoms: Sharp pain, nausea, and back pain.
- When to seek help: If pain prevents normal daily activities.
Menorrhagia (Heavy Bleeding)
- Cause: Hormonal imbalance, fibroids, or thyroid issues.
- Symptoms: Very heavy flow, fatigue, and weakness.
- When to seek help: If bleeding lasts more than 7 days or causes anemia.
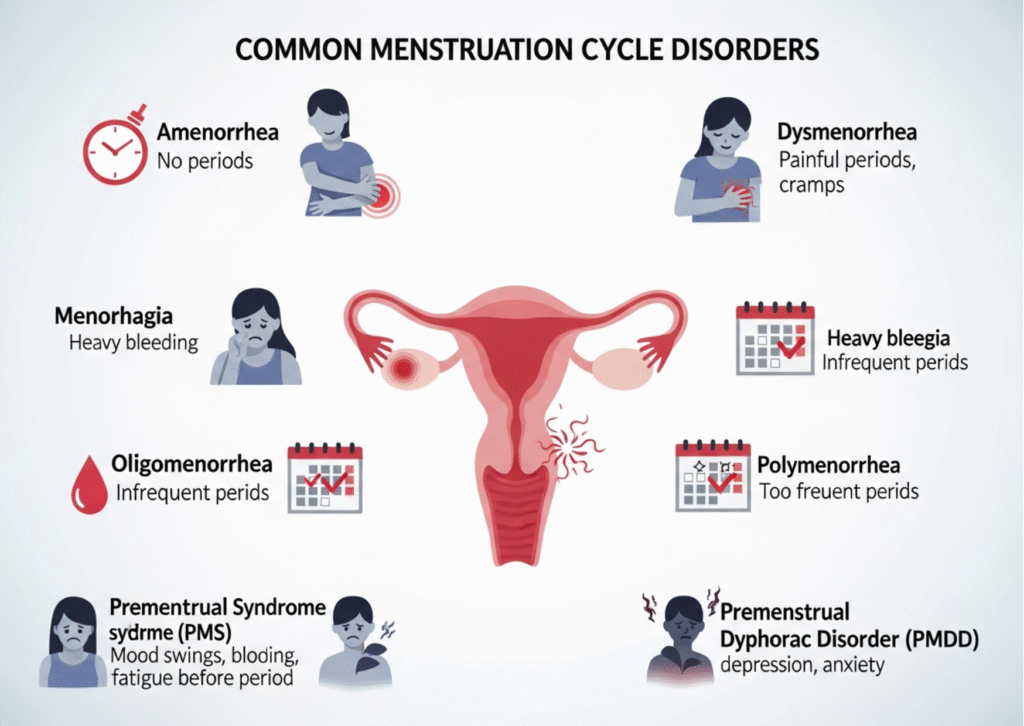
Amenorrhea (No Periods)
- Cause: Stress, pregnancy, weight changes, PCOS, or hormonal issues.
- Symptoms: Missed periods for 3+ months.
- When to seek help: Always it needs evaluation.
PMS (Premenstrual Syndrome)
- Cause: Hormone shifts before the period.
- Symptoms: Mood swings, bloating, sadness, irritability.
- Help: Exercise, rest, healthy diet, stress reduction.
PMDD (Severe Mood Disorder Before Periods)
- Cause: Extreme sensitivity to hormonal changes.
- Symptoms: Severe depression, anger, or anxiety before menstruation.
- Seek medical help: If emotional symptoms are intense.
PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome)
- Cause: Hormonal imbalance affecting ovulation.
- Symptoms: Irregular periods, acne, weight gain, unwanted hair growth.
- Medical care: Required for long-term health.
Endometriosis
- Cause: Tissue similar to the uterus lining grows outside the uterus.
- Symptoms: Severe pain, painful sex, fertility issues.
- Seek specialist care: Required if symptoms are persistent.
How Doctors Diagnose Menstruation Cycle Issues
Doctors may use:
- Medical history discussion
- Physical and pelvic examination
- Hormone level tests
- Ultrasound to check ovaries and uterus
- Sometimes MRI or laparoscopy for complex cases
Treatment Options
| Treatment Type | Purpose |
| Pain Relief Medicines | Reduce cramps and discomfort. |
| Hormonal Therapy / Birth Control Pills | Regulate hormones and control bleeding. |
| Diet and Lifestyle Changes | Reduce symptoms and support hormone balance. |
| Iron Supplements | Used if heavy bleeding causes anemia. |
| Surgery | Only for conditions like fibroids or endometriosis when severe. |
Healthy Care Guide for Menstrual Well-Being
- Maintain good hygiene and change pads/tampons regularly.
- Eat iron-rich foods like spinach, meat, beans, and dates.
- Drink plenty of water to reduce bloating and fatigue.
- Do light exercise such as walking or yoga.
- Get enough sleep and manage stress.
- Talk openly periods are normal, not shameful.
Doctors’ Roles in Menstruation Cycle and Reproductive Health
| Doctor Type | Role in Menstrual Health | When to Visit |
|---|---|---|
| Gynecologist | Specializes in female reproductive system; diagnoses and treats menstrual disorders, PCOS, endometriosis, infertility, and hormonal issues. | Irregular cycles, severe pain, heavy bleeding, missed periods, pregnancy concerns. |
| Endocrinologist | Treats hormonal imbalances affecting the menstrual cycle such as thyroid disorders, PCOS, or pituitary gland issues. | If cycles are irregular due to hormone imbalance, weight changes, or PCOS symptoms. |
| Primary Care Doctor (General Physician) | Performs initial evaluation, basic tests, and can refer to specialists if needed. | For mild menstrual pain, routine checkups, or questions about period health. |
| Psychologist / Therapist | Provides emotional and mental health support for PMS, anxiety, PMDD, or stress-related cycle issues. | If mood swings, stress, or emotional symptoms interfere with daily life. |
| Nutritionist / Dietitian | Helps plan meals that support healthy hormone levels and reduce period symptoms (iron-rich, balanced diet). | If diet is poor, anemia occurs, or weight changes are affecting the cycle. |
Powerful Reminder
“The menstrual cycle is not just a monthly event it is a vital sign of a woman’s overall health.”
Appoint Doctor:
Need Help or Consultation? Book Your Appointment Here: Gynecologist
What is the normal length of a menstrual cycle?
A normal menstrual cycle usually lasts between 21 to 35 days, counting from the first day of one period to the first day of the next. Slight variations month-to-month are common.
Is it normal to have pain during periods?
Yes, mild to moderate cramps are normal because the uterus contracts to shed its lining. However, severe pain that affects daily activities may indicate conditions like dysmenorrhea or endometriosis and should be checked by a doctor.
Why do some people have irregular periods?
Irregular cycles can be caused by stress, weight changes, poor nutrition, hormonal imbalance, PCOS, thyroid problems, or excessive exercise. A medical evaluation helps identify the cause.
Can exercise or diet affect the menstrual cycle?
Yes. Regular exercise, good sleep, and balanced nutrition help maintain a healthy cycle. Poor diet, extreme dieting, or intense workouts may disrupt hormones and lead to irregular periods.
When should someone see a doctor about their periods?
If periods are very painful, too heavy, come too frequently, are missing for 3 months or more, or cause major mood or energy changes, it is important to consult a Gynecologist for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Pingback: Tuberculosis: Causes and How It Spread