Diabetes is one of the most common long-term health conditions in the world today. Millions of people live with it, and many more are at risk without realizing it. Understanding diabetes is important because early awareness and healthy lifestyle changes can help prevent serious complications in the future. Let’s explore diabetes in a simple, clear, and helpful way.

What Is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a condition in which the body has trouble controlling the level of sugar (glucose) in the blood. Normally, when we eat food, especially carbohydrates, the body breaks it down into glucose. This glucose enters the bloodstream and the hormone insulin, produced by the pancreas, helps move glucose into the cells where it is used for energy.
In diabetes, the body either:
- Does not produce enough insulin, or
- Cannot use insulin properly (called insulin resistance).
As a result, sugar stays in the blood instead of entering the cells. Over time, high blood sugar can damage the heart, kidneys, eyes, nerves, and other organs.
Also read about this: Diabetes
Remember:https://healthytipspro.com/nutrition-nourishing-your-body-for-a-healthier-life/
Types of Diabetes
There are several types of diabetes, and each has different causes.
Type 1 Diabetes
This type happens when the immune system mistakenly attacks the pancreas, stopping it from making insulin. People with Type 1 need insulin injections for life. It often appears in childhood or early adulthood.
Type 2 Diabetes
This is the most common type. The body still makes insulin, but it does not use it effectively. This is called insulin resistance. It is often linked to:
- Lack of physical activity
- Being overweight
- Unhealthy eating habits
- Stress
- Family history
Type 2 diabetes usually develops slowly over many years.
Gestational Diabetes
This occurs during pregnancy when the body cannot manage blood sugar properly. It usually disappears after childbirth, but it increases the mother’s and baby’s risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later in life.
Prediabetes
This is a warning stage where blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough for diabetes. Prediabetes can often be reversed with healthy lifestyle changes.
How Common Is Diabetes?
Diabetes rates have been rising worldwide. Modern lifestyles play a big role eating fast food, sitting for long hours, lack of exercise, stress, and weight gain all contribute to the increasing number of cases. Today, diabetes can affect anyone children, adults, and older individuals alike.
Symptoms of Diabetes
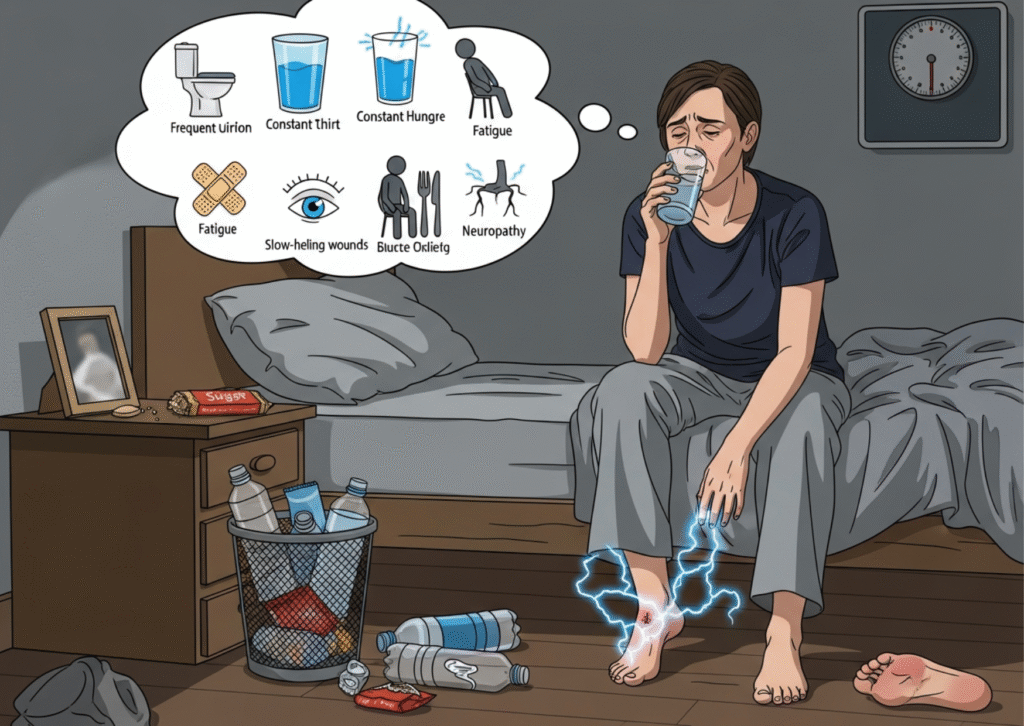
Many symptoms develop slowly, so diabetes can go unnoticed for years. Common signs include:
- Frequent urination
- Constant thirst
- Increased hunger
- Fatigue or low energy
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing wounds or infections
- Tingling or numbness in hands and feet
- Unexplained weight loss (especially in Type 1)
If you notice these symptoms, it’s important to check your blood sugar.
What Causes Diabetes?
The causes of diabetes depend on the type:
- Type 1: Caused by an autoimmune reaction where the body attacks insulin-producing cells. The exact cause is not known, but genetics play a role.
- Type 2: Usually develops because of lifestyle factors like lack of activity, unhealthy eating, weight gain especially around the belly and genetics.
- Gestational: Caused by hormonal changes during pregnancy.
Regardless of the cause, the result is the same the body cannot manage blood sugar properly.
Complications of Diabetes
If diabetes is not controlled, high blood sugar can damage many parts of the body, including:
- Heart and blood vessels (risk of heart disease and stroke)
- Kidneys (kidney failure)
- Nerves (numbness, pain, or burning sensation)
- Eyes (vision loss or blindness)
- Feet (ulcers and infections that may require amputation)
These complications develop slowly over time, which is why early diagnosis and consistent care are essential.
How Is Diabetes Diagnosed?
Doctors use several tests to diagnose diabetes:
- Fasting Blood Sugar Test: Measures blood sugar after not eating overnight.
- HbA1c Test: Shows your average blood sugar level over the past 2–3 months.
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test: Measures how the body handles sugar after drinking a sugary liquid.
These tests help confirm whether someone has normal blood sugar, prediabetes, or diabetes.
How Is Diabetes Managed?
Managing diabetes means keeping blood sugar within a healthy range. Key steps include:
- Healthy eating: Focus on whole grains, vegetables, lean proteins, fruits, and healthy fats. Avoid sugary drinks and processed foods.
- Regular exercise: Even 30 minutes of walking daily improves blood sugar control.
- Weight management: Losing even a small amount of weight can improve insulin function.
- Medications: Many people with Type 2 diabetes take medications like Metformin. Some may need insulin.
- Monitoring blood sugar: Checking levels regularly helps manage changes in diet, activity, and stress.
- Routine check-ups: Doctors can help prevent or manage complications early.
Diabetes management is not about perfection it’s about consistent healthy habits.
What Is the Prognosis?
With proper care, people with diabetes can live long, active, and fulfilling lives. Many complications can be avoided by staying aware and managing blood sugar. However, if diabetes is ignored, the risk of serious health problems increases.
The key is to understand your condition and take control step by step.
How Can I Prevent Diabetes?
You can greatly reduce your risk by making healthier choices:
- Eat more whole foods and fewer processed snacks
- Exercise regularly walking is a great start
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Drink water instead of sugary drinks
- Get enough sleep and manage stress
- Have regular health check-ups, especially if diabetes runs in your family
Small daily changes matter more than sudden big ones.
Living a healthy life with diabetes or preventing it starts with awareness. Every meal, every walk, and every small decision adds up. Your health is in your hands, and even one positive change can lead to a healthier future. You don’t have to be perfect just take it one day at a time.
Diabetes Diet – What to Eat and What to Avoid

| Category | Foods to Eat (Healthy Choices) | Foods to Avoid (Unhealthy / High Sugar) |
| Grains & Carbs | Whole wheat roti, brown rice, oats, quinoa, barley, multigrain bread | White rice, white bread, naan, paratha, pasta, pastries, refined flour items (Maida) |
| Vegetables | Leafy greens, broccoli, carrots, cucumber, bottle gourd, bitter gourd, beans, cauliflower | Potatoes (large amounts), sweet corn, deep-fried vegetables |
| Fruits | Apples, papaya, guava, pear, oranges, berries (small portions) | Mangoes (large portions), bananas (large portions), grapes, fruit juices, dried fruits with sugar |
| Protein | Grilled chicken, fish, lentils, beans, chickpeas, tofu, eggs (boiled/steamed) | Fried chicken, processed meats (sausages, nuggets), high-fat red meat |
| Dairy | Low-fat milk, yogurt (unsweetened), paneer in moderation | Full cream milk, ice cream, flavored yogurt, sweetened milk drinks |
| Healthy Fats | Nuts (almonds, walnuts), seeds (chia, flaxseed), olive oil, coconut in moderation | Ghee (too much), butter, margarine, fried food, bakery items |
| Drinks | Water, green tea, black coffee (no sugar), lemon water | Soft drinks, energy drinks, sugary tea/coffee, packaged juices |
| Snacks | Roasted chickpeas, nuts, boiled eggs, vegetables with hummus | Chips, biscuits, chocolate, cakes, fast food snacks |
| Sweeteners | Use small amounts only if needed | White sugar, honey (excess), jaggery, syrup |
Simple Daily Meal Pattern (Example)
| Meal | Suggestion |
| Breakfast | Oats with chia seeds + boiled egg OR Multigrain roti + vegetable omelet |
| Lunch | 1–2 chapatti (whole wheat) + lentils + mixed vegetables + salad |
| Snack | Green tea + handful of nuts OR Roasted chickpeas |
| Dinner | Grilled chicken/fish or lentils + vegetables + small portion of brown rice or roti |
| Before Bed (if needed) | A cup of warm unsweetened milk |
Important Tips
- Eat small, frequent meals instead of big heavy ones.
- Avoid sugar completely even small hidden sugar adds up.
- Drink plenty of water.
- Walk 15–30 minutes daily, especially after meals.
Doctor’s Role in Diabetes Management
| Doctor’s Role | What the Doctor Does | Why It Is Important |
| Diagnosis & Evaluation | Orders blood tests such as Fasting Sugar, HbA1c, and Glucose Tolerance Test | Helps confirm diabetes early before complications develop |
| Creating a Treatment Plan | Suggests diet, exercise routine, medications, or insulin based on the patient’s condition | Ensures treatment is personalized and effective |
| Medication & Insulin Management | Prescribes medicines like Metformin or advises insulin use when required | Keeps blood sugar under control and prevents organ damage |
| Monitoring Complications | Checks heart health, kidneys, eyes, nerves, and feet during follow-ups | Helps detect problems at early stages to avoid serious damage |
| Lifestyle Guidance | Advises on weight control, physical activity, stress management, and sleep habits | Supports long-term health and improves quality of life |
| Patient Education | Teaches how to monitor blood sugar, use insulin pens, and manage low/high sugar episodes | Empowers the patient to manage diabetes confidently |
| Regular Follow-Up Appointments | Schedules routine checkups every 3–6 months | Ensures diabetes remains under control and treatment stays up to date |
Appoint Doctor:
If you are experiencing diabetes symptoms or need a personalized treatment plan, consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and guidance: Click Now Endocrinologist
Can diabetes be cured?
Diabetes cannot be completely cured, but it can be well-controlled. With a healthy diet, exercise, weight management, and medication, many people live normal, active lives. In some cases of Type 2 diabetes, blood sugar can return to normal through lifestyle changes, but it still requires monitoring.
What is the main cause of diabetes?
The cause depends on the type.
Type 1 happens when the immune system destroys insulin-producing cells.
Type 2 usually develops due toinsulin resistance, which is linked to being overweight, lack of exercise, poor diet, stress, and genetics.
Family history also plays a strong role in both types.
Is diabetes hereditary?
Yes, diabetes can run in families. Having a parent or sibling with diabetes increases your risk. However, lifestyle choices like eating healthy and staying active can help reduce your chances.
What foods increase blood sugar the fastest?
Sugary foods and refined carbohydrates raise blood sugar quickly. Examples include:
White rice
White bread
Sweets
Sugary drinks
Cakes and biscuits
These foods digest fast and cause blood sugar to spike.
How often should I check my blood sugar?
It depends on the type of diabetes and treatment plan:
People taking insulin may need to check multiple times a day.
Others may only need to check once or a few times a week.
Your doctor will guide you based on your condition, medications, and lifestyle.
Pingback: Airborne Diseases